The area of geometric figures represents the region covered by the figure in space. The area is one of the most important measurements of geometric figures. Area is a two-dimensional measure, so it has square units, such as m², cm², and so on. We can calculate the area of both two-dimensional figures and three-dimensional figures. The formula for the area depends on the shape of the figure and its dimensions.
Here, we will learn about the formulas for the areas of the most important geometric figures. Then, we will apply these formulas to solve some problems.
Definition of area
The area of a geometric figure is defined as the region occupied by a figure in space. Area is one of the most important measurements of geometric figures. Since area is a two-dimensional measure, we use square units to measure it. For example, we can use m², cm², and so on.
The area can be calculated from a 2D figure, as well as from a 3D figure. In the case of the 3D figure, the area is called the surface area and it is the area of all the faces of the figure. For two figures to have the same area, their shape and dimensions must be the same.
Formulas for the area of 2D figures
The area formulas depend on the shape of the 2D figure. The most important 2D figures are the square, triangle, rectangle, circle, parallelogram, trapezium, and ellipse.
Area of a rectangle
A rectangle is a figure that has four 90° interior angles. The opposite sides of a rectangle are the same length.
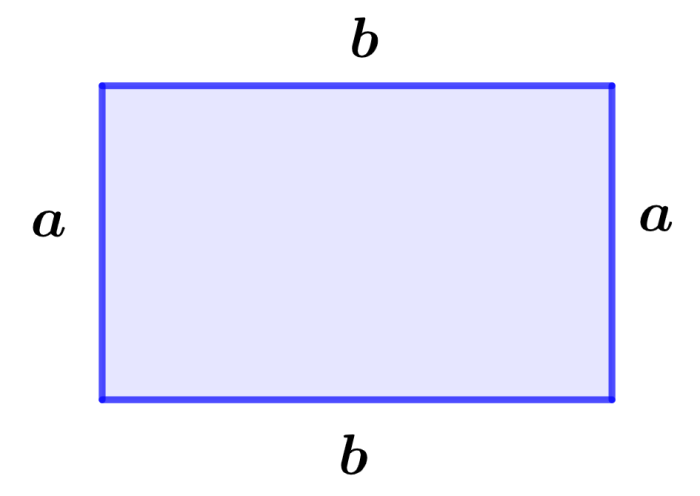
Area of rectangle = a×b
where, a represents the width of the rectangle and b represents its length.
Area of a square
A square is defined as a special type of rectangle that has all its sides the same length.
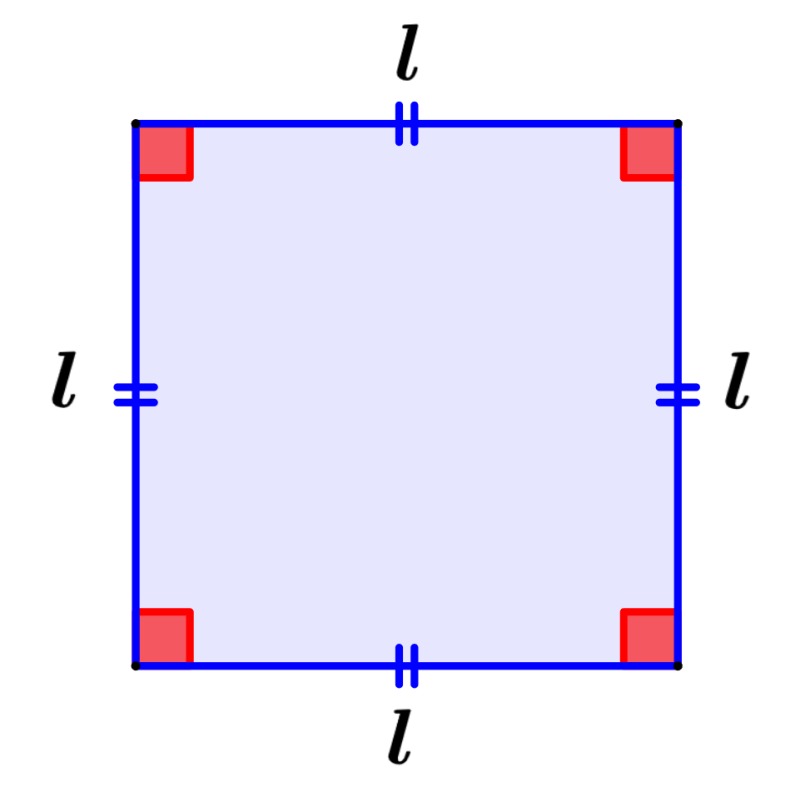
Area of a square = l²
where l represents the length of one of the sides of the square.
Area of a triangle
A triangle is defined as a three-sided polygon. There are three main types of triangles: equilateral, isosceles, and scalene. However, the area formula applies to any type of triangle.
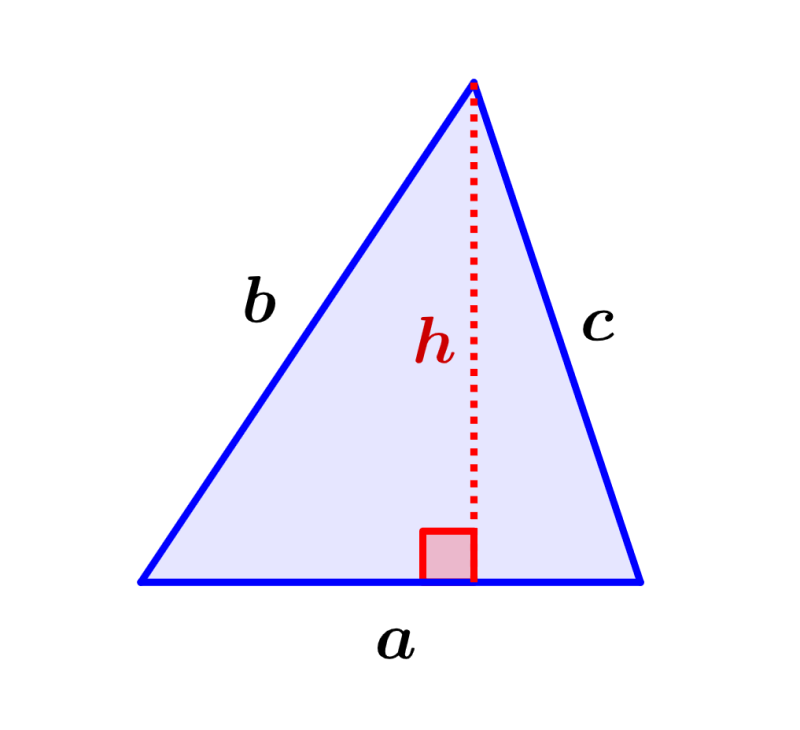
Area of a triangle = ½ha
where, h represents the height and a represents the base of the triangle.
Area of a circle
The circle is defined as the set of points that are located at the same distance from a central point. That distance is called the radius and is used to calculate the area of the circle.
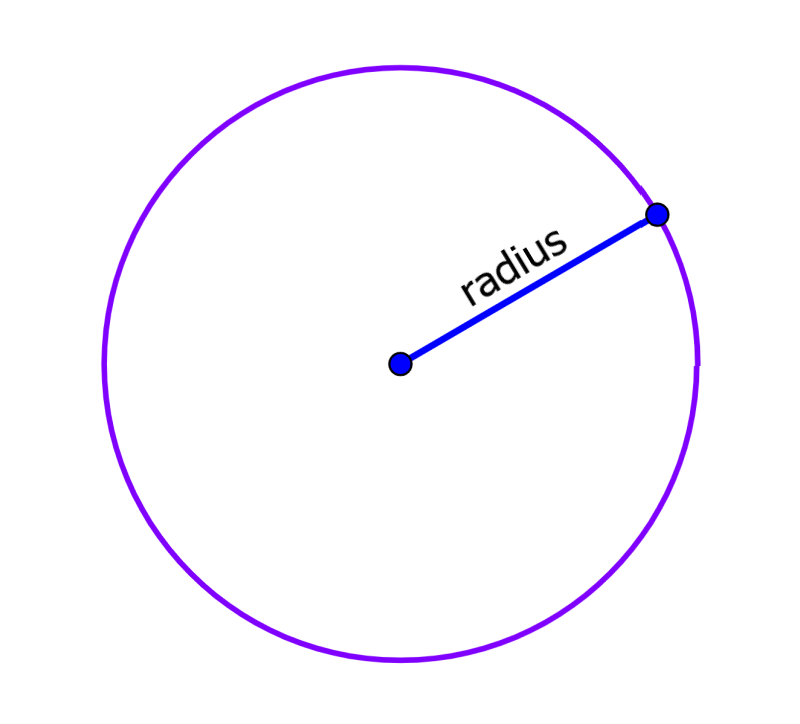
Area of a circle = πr²
where r represents the radius and π is a numerical constant with an approximate value of 3.1415…
Area of a parallelogram
The parallelogram is a figure in which its opposite sides are parallel to each other. The height of the parallelogram is used to calculate its area.
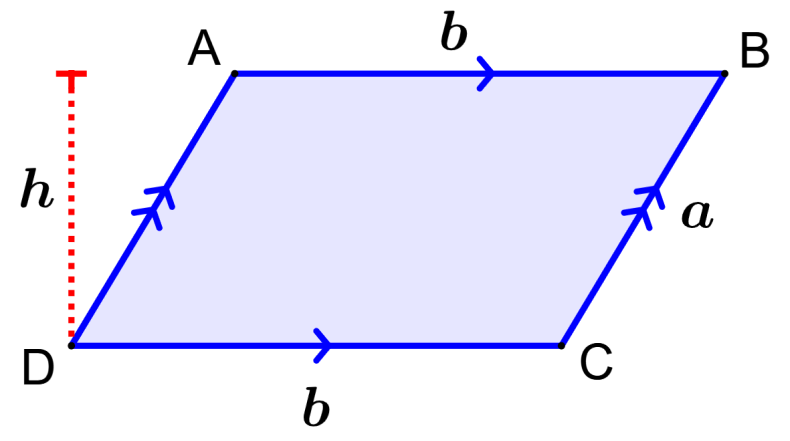
Area of a parallelogram: bh
where b is the length of the base and h is the length of the height.
Area of a trapezium
The trapezium is a four-sided figure in which at least two of its sides are parallel. The parallel sides are called the bases of the trapezoid.
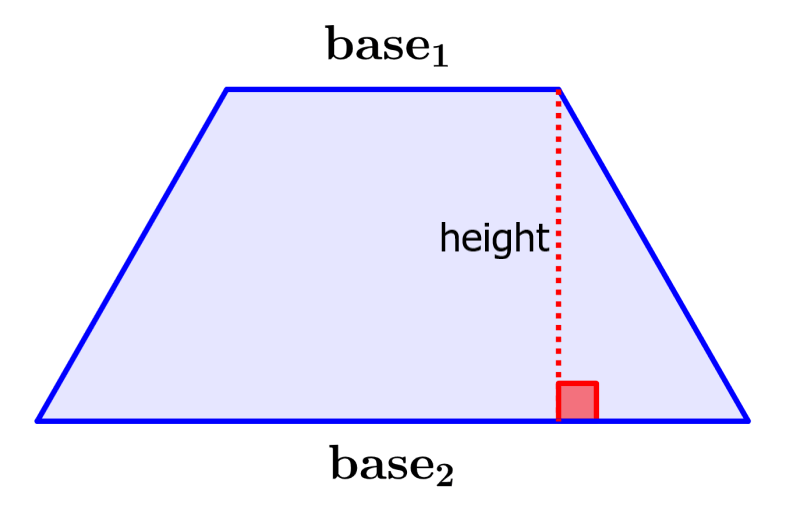
Area of a trapezium: $latex \frac{a + b}{2} h$
where a and b are the lengths of both bases and h is the height of the trapezium.
Area of an ellipse
An ellipse is a figure that has an elongated circular shape.
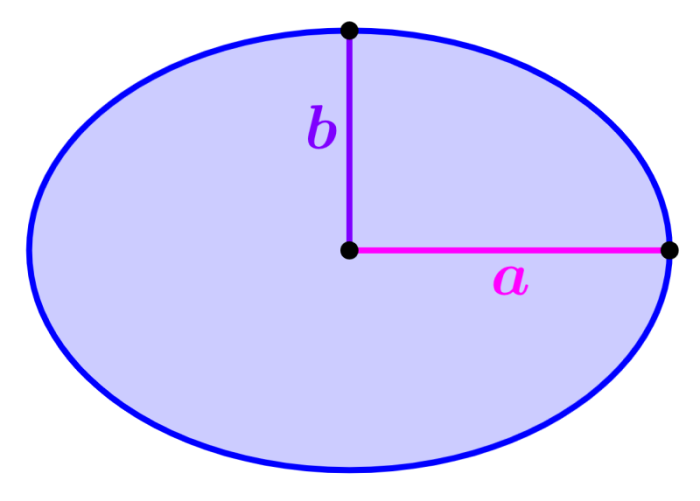
Area of an ellipse: πab
where a is half the length of the major axis and b is half the length of the minor axis.
| Figure | Area | Terms |
| Circle | A = πr² | r=radius |
| Triangle | A = ½ bh | b=base, h=height |
| Square | A = l² | l=length of one side |
| Rectangle | A = ab | a=width, b=base |
| Parallelogram | A = bh | b=base, h=height |
| Trapezium | A = $latex \frac{a+b}{2}h$ | a and b=bases, h=height |
| Ellipse | A = πab | a=½ major axis, b=½ minor axis |
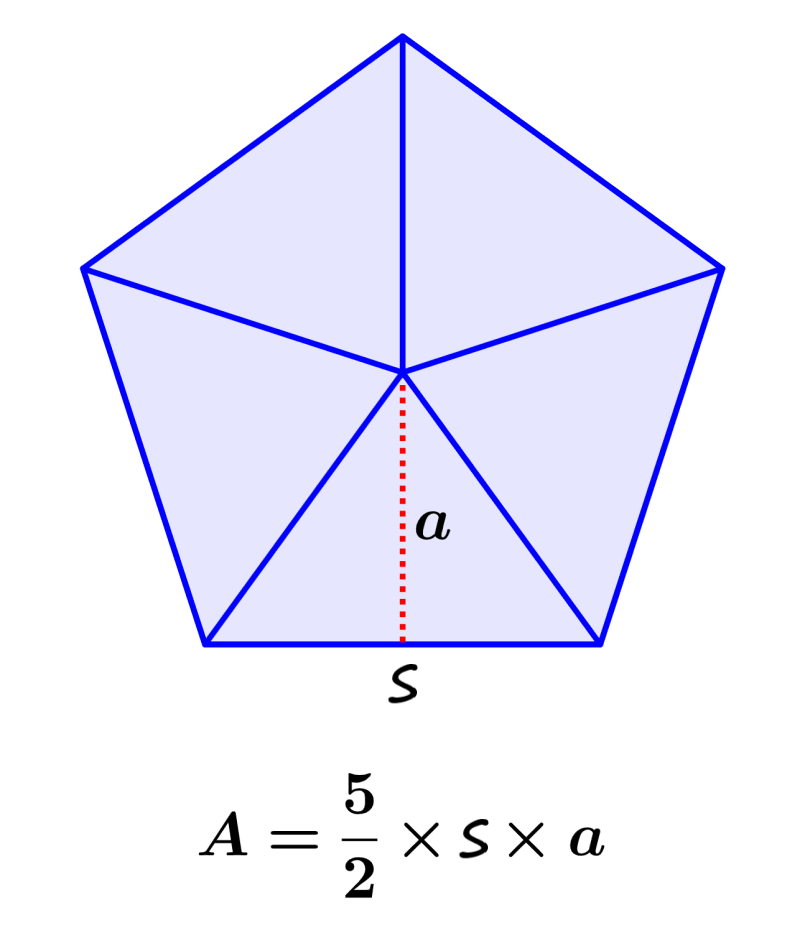
| Regular polygon | A = ½ nla | n=n° of sides, l=length of side, a=apothem |
Formulas for the area of 3D figures
In the case of 3D figures, their area is called the surface area. The most important 3D figures are the cube, the rectangular prism, the cylinder, the cone, the sphere, the triangular pyramid, and the rectangular pyramid.
Area of a cube
A cube is a three-dimensional figure that has all its sides of equal length. A cube has a total of six square faces and its area is equal to the sum of all the faces.
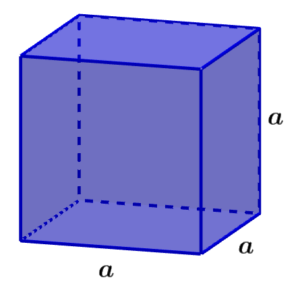
Area of a cube = 6a²
where a is the length of one of the sides of the cube.
Area of a rectangular prism
The rectangular prism is a 3D figure with six rectangular faces. The opposite faces of a rectangular prism are equal.
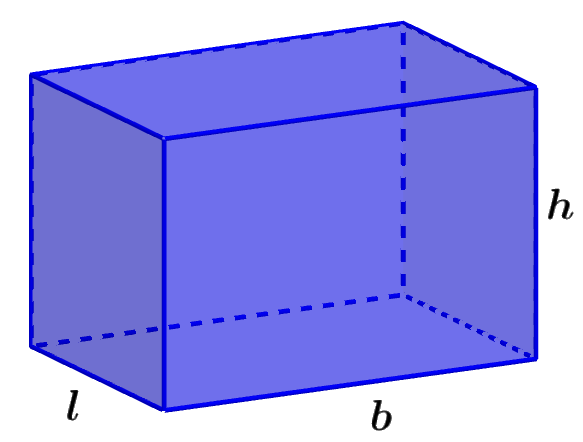
Area of a rectangular prism = 2(lb+lh+hb)
where l is the length of the width, b is the length of the base, and h is the length of the height.
Area of a cylinder
A cylinder is a three-dimensional figure that has two circular bases, which are joined and covered by a surface.
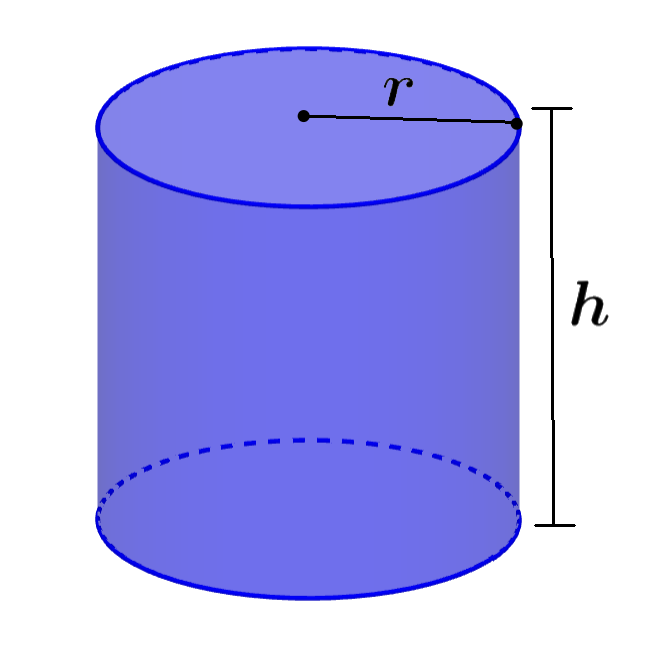
Area of a cylinder = 2πr(r+h)
where r is the radius of one of the cylinder faces, h is the height and π is a mathematical constant with a value of approximately 3.1415…
Area of a triangular pyramid
A triangular pyramid is a three-dimensional figure that has four triangular faces, which is why it is also called a tetrahedron.
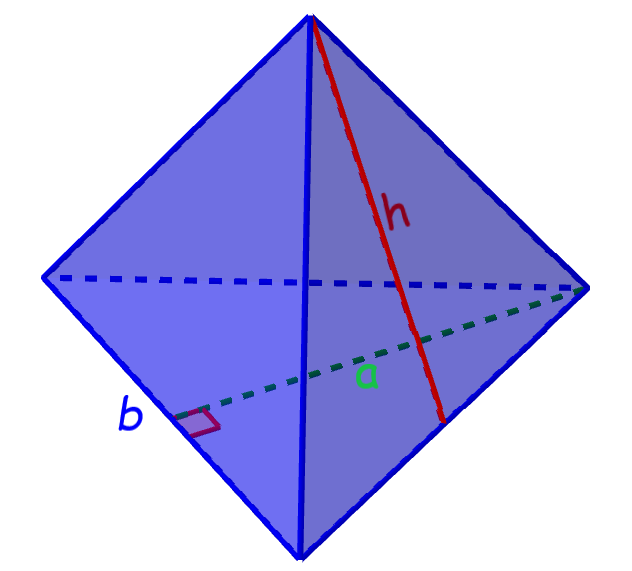
Area of a triangular pyramid = $latex \frac{1}{2} ba + \frac{3}{2} bh$
where b is the length of one of the sides of the base, a is the height of the triangle at the base, and h is the height of one of the lateral triangles.
Area of a rectangular pyramid
A rectangular pyramid is a figure that has a rectangular base and four lateral triangular faces.
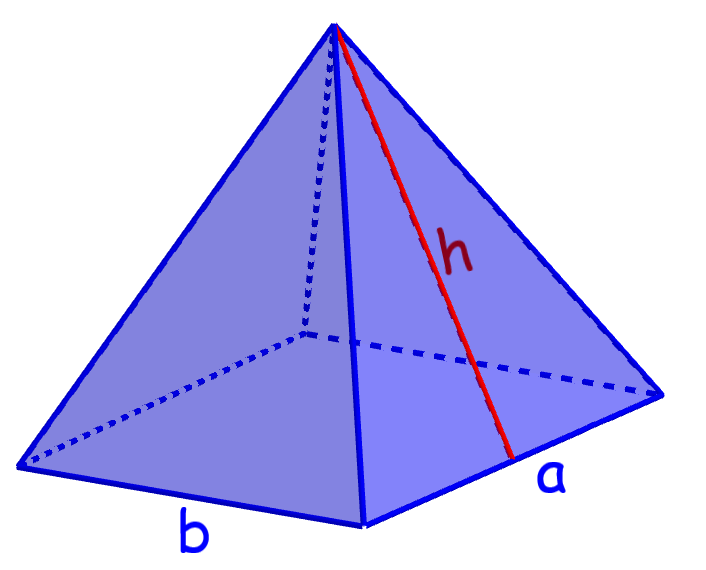
Area of a rectangular pyramid = ba+bh+ah
where, a and b are the lengths of the rectangular base and h is the height of a triangular side face.
Area of a sphere
A sphere is a three-dimensional figure that is perfectly round. Each point on the sphere is located at the same distance from the center.
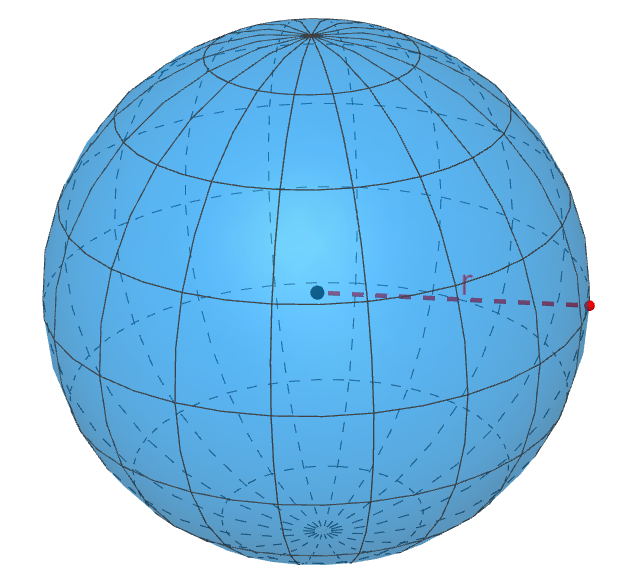
Area of a sphere = 4πr²
where r is the radius of the sphere and π is a numerical constant that has a value of 3.1415…
| Figure | Area | Terms |
| Cube | A = 6a² | a=length of a side |
| Rectangular prism | A = 2(lb+lh+hb) | l=width, b=base, h=height |
| Cylinder | A = 2πr(r+h) | r=radius of bases, h=height |
| Triangular pyramid | A = $latex \frac{1}{2}ba+\frac{3}{2}bh$ | b=sides of base, a=height of base, h=height of lateral sides |
| Rectangular pyramid | A = ba+bh+ah | a and b=sides of base, h=height of lateral sides |
| Cone | A = πr(r+l) | r=radius of base, l=slant height |
| Sphere | A = 4πr² | r=radius |
See also
Interested in learning more about geometric figures? Take a look at these pages: