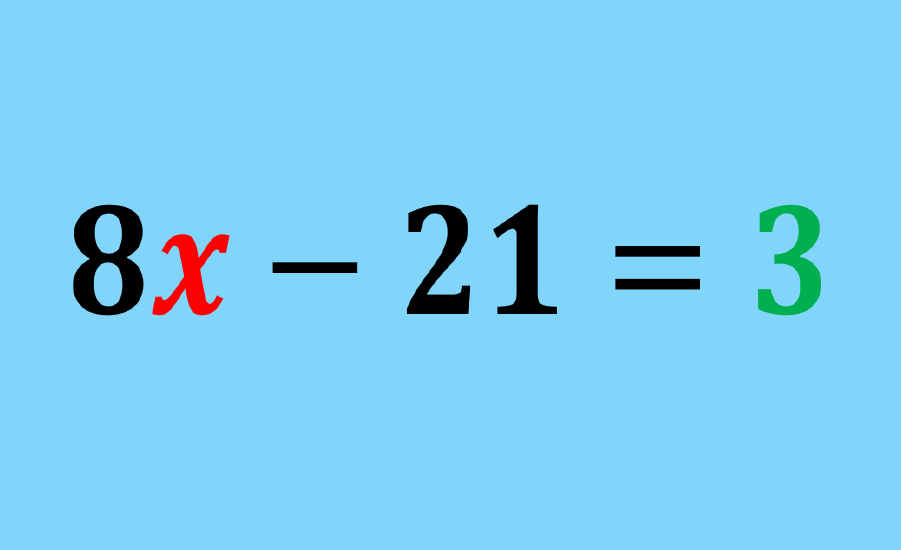Linear equations can be solved by applying various operations to both sides of the equal sign. These operations can help us simplify the equation, solve for the variable, and ultimately find the solution.
In this article, we will look at a brief summary of linear equations, followed by 20 examples with answers to master the process of solving first-degree equations.
How to solve linear equations?
Recall that linear equations are equations in which all variables have a maximum power of 1. For example, the equations $latex 4x+1=5$ and $latex 2x+12=4x-2$ are linear equations.
To solve linear equations, we have to apply different operations to both sides of the equal sign, so that we can solve for the variable. Therefore, we can follow the following steps to find the solution to linear equations:
Step 1: We simplify the expression. This includes removing parentheses and other grouping signs, removing fractions, and combining like terms.
Step 2: We isolate the variable. We perform addition and subtraction to place all terms with variables on only one side of the equation.
Step 3: We solve the equation. We do multiplication and division to find the answer.
20 Linear equation examples with answers
The following 20 linear equation examples have their respective solution, where the process is indicated step by step. It is recommended that you try to solve the examples yourself before looking at the answer.
EXAMPLE 1
Solve the equation $latex 5x-12=3$.
Solution
Step 1: Simplify: We have nothing to simplify here.
Step 2: Solve for the variable: We use addition to solve for the variable:
$latex 5x-12=3$
$latex 5x-12+12=3+12$
$latex 5x=15$
Step 3: Solve: We divide both sides by 5:
$$\frac{5x}{5}=\frac{15}{5}$$
$latex x=3$
EXAMPLE 2
Solve the equation $latex 3x+1=x-3$.
Solution
Step 1: Simplify: We have nothing to simplify.
Step 2: Solve for the variable: We use addition and subtraction to solve for the variable:
$latex 3x+1=x-3$
$latex 3x+1-1=x-3-1$
$latex 3x=x-4$
$latex 3x-x=x-4-x$
$latex 2x=-4$
Step 3: Solve: We divide both sides by 2:
$$\frac{2x}{2}=\frac{-4}{2}$$
$latex x=-2$
EXAMPLE 3
Find the value of t in the equation $latex 5t+5=3t+7$.
Solution
Step 1: Simplify: We do not have like terms.
Step 2: Solve for the variable: We use subtraction to solve for the variable:
$latex 5t+5=3t+7$
$latex 5t+5-5=3t+7-5$
$latex 5t=3t+2$
$latex 5t-3t=3t+2-3t$
$latex 2t=2$
Step 3: Solve: We divide both sides by 2:
$$\frac{2t}{2}=\frac{2}{2}$$
$latex t=1$
EXAMPLE 4
Solve the equation $latex 3(2x+1)=-9$.
Solution
Step 1: Simplify: We expand the parentheses:
$latex 3(2x+1)=-9$
$latex 6x+3=-9$
Step 2: Solve for the variable: We use subtraction to solve for the variable:
$latex 6x+3=-9$
$latex 6x+3-3=-9-3$
$latex 6x=-12$
Step 3: Solve: We divide both sides by 6:
$$\frac{6x}{6}=\frac{-12}{6}$$
$latex x=-2$
EXAMPLE 5
Solve the equation $latex 2(2x-5)=3(x-1)-4$.
Solution
Step 1: Simplify: We expand the parentheses on both sides of the equation and combine like terms:
$latex 2(2x-5)=3(x-1)-4$
$latex 4x-10=3x-3-4$
$latex 4x-10=3x-7$
Step 2: Solve for the variable: We use addition and subtraction to solve for the variable:
$latex 4x-10+10=3x-7+10$
$latex 4x=3x+3$
$latex 4x-3x=3-3x$
$latex x=3$
Step 3: Solve: In this case, we no longer have to divide:
$latex x=3$
EXAMPLE 6
Find the value of z in the equation $latex 3(z-2)+10=2(2z+2)+2$.
Solution
Step 1: Simplify: We expand the parentheses and combine like terms:
$latex 3(z-2)+10=2(2z+2)+2$
$latex 3z-6+10=4z+4+2$
$latex 3z+4=4z+6$
Step 2: Solve for the variable: We use subtraction to solve for the variable:
$latex 3z+4-4=4z+6-4$
$latex 3z=4z+2$
$latex 3z-4z=2$
$latex -z=2$
Step 3: Solve: We divide both sides by -1:
$$\frac{-z}{-1}=\frac{2}{-1}$$
$latex z=-2$
EXAMPLE 7
Solve the equation $latex \frac{2x+1}{3}=x-1$.
Solution
Step 1: Simplify: We multiply by 3 to eliminate the fraction:
$$\frac{2x+1}{3}=x-1$$
$latex 2x+1=3x-3$
Step 2: Solve for the variable: We subtract 1 and 3x from both sides:
$latex 2x+1=3x-3$
$latex 2x+1-1=3x-3-1$
$latex 2x=3x-4$
$latex 2x-3x=3x-4-3x$
$latex -x=-4$
Step 3: Solve: We divide both sides by -1:
$$\frac{-x}{-1}=\frac{-4}{-1}$$
$latex x=4$
EXAMPLE 8
Solve the equation $latex \frac{4x}{3}-2= \frac{2x+3}{3} -1$.
Solution
Step 1: Simplify: We multiply both sides of the equation by 3 to eliminate the fractions and combine like terms:
$$\frac{4x}{3}-2=\frac{2x+3}{3}-1$$
$latex 4x-6=2x+3-3$
$latex 4x-6=2x$
Step 2: Solve for the variable: We add 6 and subtract 2x from both sides:
$latex 4x-6+6=2x+6$
$latex 4x=2x+6$
$latex 4x-2x=2x+6-2x$
$latex 2x=6$
Step 3: Solve: We divide both sides by 2:
$$\frac{2x}{2}=\frac{6}{2}$$
$latex x=3$
EXAMPLE 9
Find the value of t in the equation $latex \frac{2t-5}{5}+2=\frac{t-2}{3}+2$.
Solution
Step 1: Simplify: We multiply by 15 to eliminate the fractions and combine like terms:
$$\frac{2t-5}{5}+2=\frac{t-2}{3}+2$$
$$3(2t-5)+15(2)=5(t-2)+15(2)$$
$latex 6t-15+30=5t-10+30$
$latex 6t+15=5t+20$
Step 2: Solve for the variable: We subtract 15 and 5 t from both sides:
$latex 6t+15=5t+20$
$latex 6t+15-15=5t+20-15$
$latex 6t=5t+5$
$latex 6t-5t=5t+5-5t$
$latex t=5$
Step 3: Solve: We no longer have to divide:
$latex t=5$
EXAMPLE 10
Solve the equation $latex \frac{2x-3}{x+1}+2=3$.
Solution
Step 1: Simplify: We multiply both sides by (x+1) and combine like terms:
$$\frac{2x-3}{x+1}+2=3$$
$latex 2x-3+2(x+1)=3(x+1)$
$latex 2x-3+2x+2=3x+3$
$latex 4x-1=3x+3$
Step 2: Solve for the variable: Add 1 and subtract 3 x from both sides:
$latex 4x-1=3x+3$
$latex 4x-1+1=3x+3+1$
$latex 4x=3x+4$
$latex 4x-3x=3x+4-3x$
$latex x=4$
Step 3: Solve: We no longer have to divide:
$latex x=4$
EXAMPLE 11
Find the value of t in the equation $latex 3t+4(t-10)=t+20$.
Solution
Step 1: Simplify: We expand the parentheses and combine like terms:
$latex 3t+4(t-10)=t+20$
$latex 3t+4t-40=t+20$
$latex 7t-40=t+20$
Step 2: Solve for the variable: We add 40 and subtract t from both sides:
$latex 7t-40=t+20$
$latex 7t-40+40=t+20+40$
$latex 7t=t+60$
$latex 7t-t=t+60-t$
$latex 6t=60$
Step 3: Solve: We divide both sides by 6:
$$\frac{6t}{6}=\frac{60}{6}$$
$latex t=10$
EXAMPLE 12
Solve the equation $latex 3x+6(x+1)=3(x+1)+5$.
Solution
Step 1: Simplify: We expand the parentheses and combine like terms:
$latex 3x+6(x+1)=3(x+1)+5$
$latex 3x+6x+6=3x+3+5$
$latex 9x+6=3x+8$
Step 2: Solve for the variable: We subtract 6 and 3 x from both sides:
$latex 9x+6=3x+8$
$latex 9x+6-6=3x+8-6$
$latex 9x=3x+2$
$latex 9x-3x=3x+2-3x$
$latex 6x=2$
Step 3: Solve: We divide both sides by 6:
$$\frac{6x}{6}=\frac{2}{6}$$
$$x=\frac{1}{3}$$
EXAMPLE 13
Find the value of x in the equation $latex \frac{1}{x+2}+2=\frac{9}{4}$.
Solution
Step 1: Simplify: We multiply the entire equation by 4 (x+2) and combine like terms:
$$\frac{1}{x+2}+2=\frac{9}{4}$$
$latex 4+8(x+2)=9(x+2)$
$latex 4+8x+16=9x+18$
$latex 8x+20=9x+18$
Step 2: Solve for the variable: We subtract 20 and 9 x from both sides:
$latex 8x+20-20=9x+18-20$
$latex 8x=9x-2$
$latex 8x-9x=9x-2-9x$
$latex -x=-2$
Step 3: Solve: We divide both sides by -1:
$$\frac{-x}{-1}=\frac{-2}{-1}$$
$latex x=2$
EXAMPLE 14
Find the value of y in the equation $$2y+3(2y-5)+4=y+3(2y-2)-6$$
Solution
Step 1: Simplify: We expand the parentheses and combine like terms:
$$2y+3(2y-5)+4=y+3(2y-2)-6$$
$latex 2y+6y-15+4=y+6y-6-6$
$latex 8y-11=7y-12$
Step 2: Solve for the variable: We add 11 and subtract 7y from both sides:
$latex 8y-11=7y-12$
$latex 8y-11+11=7y-12+11$
$latex 8y=7y-1$
$latex 8y-7y=7y-1-7y$
$latex y=-1$
Step 3: Solve: We no longer have to divide:
$latex y=-1$
EXAMPLE 15
Solve the equation $latex \frac{4x-9}{3}+2=3(x-2)$.
Solution
Step 1: Simplify: We multiply the entire equation by 3, expand the parentheses, and combine like terms:
$$\frac{4x-9}{3}+2=3(x-2)$$
$latex 4x-9+6=9(x-2)$
$latex 4x-3=9x-18$
Step 2: Solve for the variable: We add 3 and subtract 9 x from both sides:
$latex 4x-3+3=9x-18+3$
$latex 4x=9x-15$
$latex 4x-9x=9x-15-9x$
$latex -5x=-15$
Step 3: Solve: We divide both sides by -5:
$$\frac{-5x}{-5}=\frac{-15}{-5}$$
$latex x=3$
EXAMPLE 16
Find the value of x in the equation $latex -3x+18=-x(13-10)+4x-2$.
Solution
Step 1: Simplify: We expand the parentheses and combine like terms:
$latex -3x+18=-x(13-10)+4x-2$
$latex -3x+18=-x(3)+4x-2$
$latex -3x+18=-3x+4x-2$
$latex -3x+18=x-2$
Step 2: Solve for the variable: We subtract 18 and subtract x from both sides:
$latex -3x+18-18=x-2-18$
$latex -3x=x-20$
$latex -3x-x=x-20-x$
$latex -4x=-20$
Step 3: Solve: We divide both sides by -4:
$$\frac{-4x}{-4}=\frac{-20}{-4}$$
$latex x=5$
EXAMPLE 17
Find the value of w in the equation $latex 10(2w-5)=2w+2(w+1)$.
Solution
Step 1: Simplify: We expand the parentheses and combine like terms:
$latex 10(2w-5)=2w+2(w+1)$
$latex 20w-50=2w+2w+2$
$latex 20w-50=4w+2$
Step 2: Solve for the variable: We add 50 and subtract 4 w from both sides:
$latex 20w-50=4w+2$
$latex 20w-50+50=4w+2+50$
$latex 20w=4w+52$
$latex 20w-4w=4w+52-4w$
$latex 16w=52$
Step 3: Solve: We divide both sides by 16 and simplify the fraction:
$$\frac{16w}{16}=\frac{52}{16}$$
$$x=\frac{13}{4}$$
EXAMPLE 18
Find the value of r in the equation $latex 3(-2r-5)+4=\frac{r}{2}+2$.
Solution
Step 1: Simplify: We multiply both sides by 2 to eliminate the fraction, expand the parentheses, and combine like terms:
$$3(-2r-5)+4=\frac{r}{2}+2$$
$latex 6(-2r-5)+8=r+4$
$latex -12r-30+8=r+4$
$latex -12r-22=r+4$
Step 2: Solve for the variable: We add 22 and subtract r from both sides:
$latex -12r-22=r+4$
$latex -12r-22+22=r+4+22$
$latex -12r=r+26$
$latex -12r-r=r+26-r$
$latex -13r=26$
Step 3: Solve: We divide both sides by -13:
$$\frac{-13r}{-13}=\frac{26}{-13}$$
$latex x=-2$
EXAMPLE 19
Find the value of x in the equation $$3x+4(-2x+1)=3(x-5)+2(2x-7)-3$$
Solution
Step 1: Simplify: We expand all the parentheses and combine like terms:
$$3x+4(-2x+1)=3(x-5)+2(2x-7)-3$$
$$ 3x-8x+4=3x-15+4x-14-3$$
$latex -5x+4=7x-32$
Step 2: Solve for the variable: We subtract 4 and 7 x from both sides:
$latex -5x+4-4=7x-32-4$
$latex -5x=7x-36$
$latex -5x-7x=7x-36-7x$
$latex -12x=-36$
Step 3: Solve: We divide both sides by -12:
$$\frac{-12x}{-12}=\frac{-36}{-12}$$
$latex x=3$
EXAMPLE 20
Find the value of x in the equation $latex 2\left(\frac{x+2}{4} \right)+2=\frac{3x}{4}+2$.
Solution
Step 1: Simplify: We start by simplifying the fraction, then multiply by 4 to eliminate the fractions and combine like terms:
$$2\left( \frac{x+2}{4}\right)+2=\frac{3x}{4}+2$$
$$\frac{x+2}{2}+2=\frac{3x}{4}+2$$
$latex 2(x+2)+8=3x+8$
$latex 2x+4+8=3x+8$
$latex 2x+12=3x+8$
Step 2: Solve for the variable: We subtract 12 and 3 x from both sides:
$latex 2x+12-12=3x+8-12$
$latex 2x=3x-4$
$latex 2x-3x=3x-4-3x$
$latex -x=-4$
Step 3: Solve: We divide both sides by -1:
$$\frac{-x}{-1}=\frac{-4}{-1}$$
$latex x=4$
See also
Interested in learning more about solving equations? Take a look at these pages: