To determine if a function is symmetric, we have to look at its graph and identify some characteristics that are unique to symmetric functions. For example, the graph can have a reflection on the x-axis, on the y-axis, or it can have rotational symmetry about the origin.
In this article, we will look at the different types of symmetry with examples to illustrate the ideas.
How to determine if a graph is symmetric?
We can determine if a graph is symmetric with respect to a line or a point if the graph does not change when it is reflected with respect to that line or is rotated around that point.
Symmetry can be useful when we want to graph an equation as it tells us that if we know a portion of the graph, then we will also know the remaining symmetric portion of the graph.
We can distinguish three main types of symmetry:
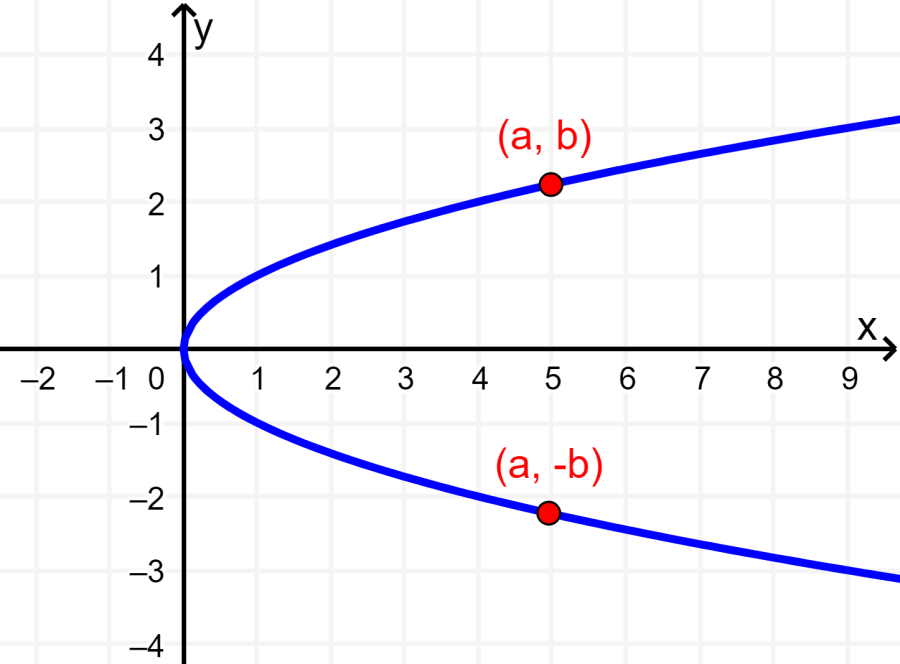
1. A graph has symmetry about the x-axis if when we have the point (a, b) on the graph, we also have the point (a, -b). The following is a graph with symmetry about the x-axis:
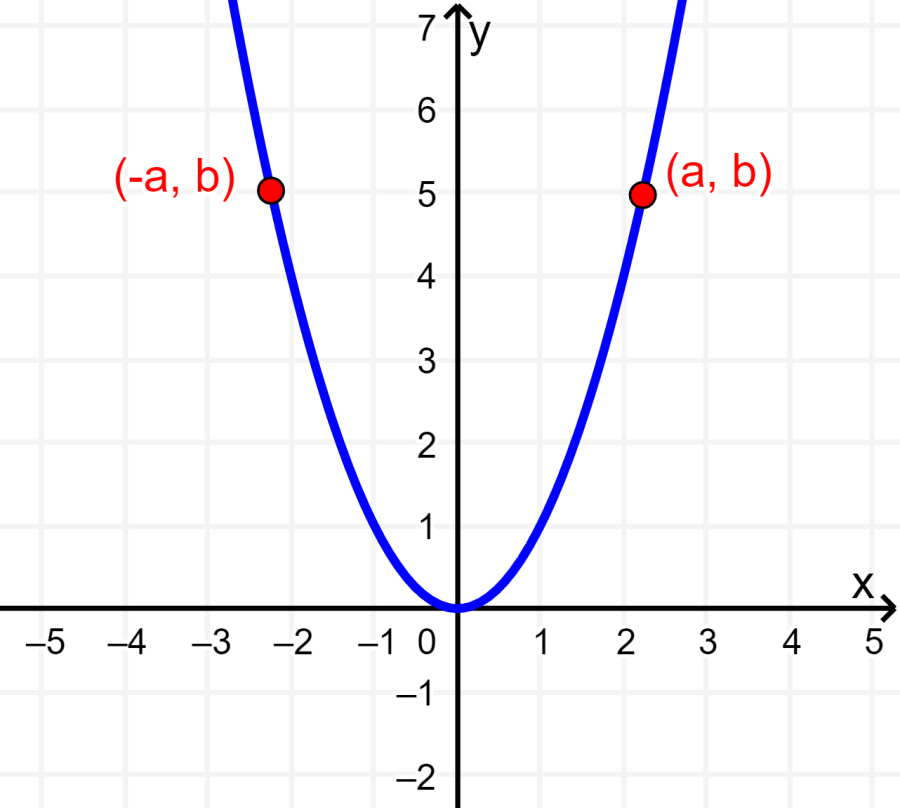
2. A graph has symmetry about the y-axis if when we have the point (a, b) on the graph, we also have the point (-a, b). The following is a graph with symmetry about the y-axis:
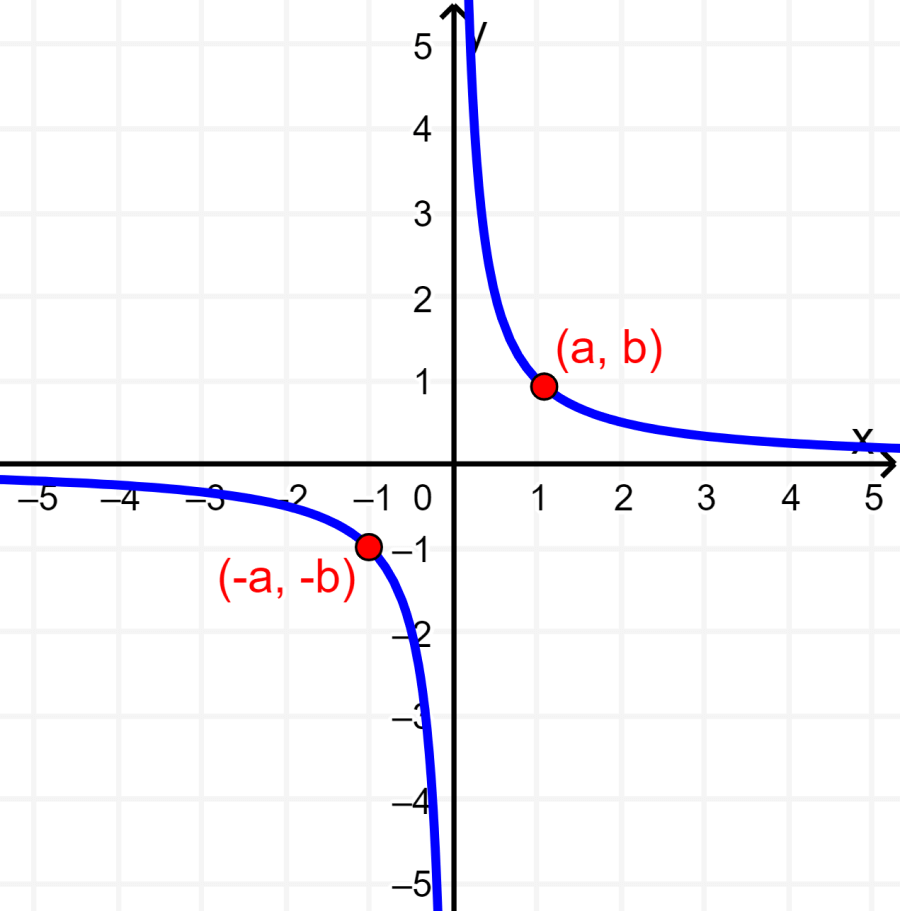
3. A graph has symmetry about the origin if when we have the point (a, b) on the graph, we also have the point (-a, -b). The following is a graph that has symmetry with respect to the origin:
Keep in mind that most graphs do not have any kind of symmetry. Furthermore, it is also possible for a graph to have more than one type of symmetry. For example, the graph of a circle centered at the origin has all three types of symmetries at the same time:
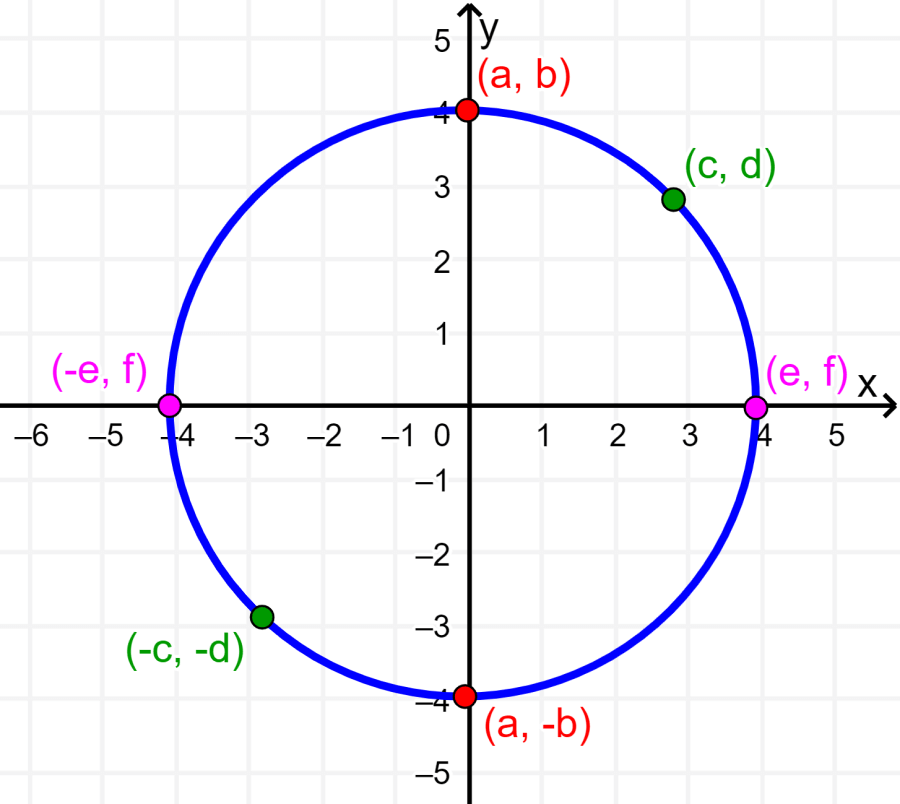
How to know if a function has odd or even symmetry?
We can distinguish two types of symmetries in the graphs of functions:
Reflection symmetry about the y-axis. This happens when we have $latex f(x)=f(-x)$.
Rotational symmetry about the origin. This happens when we have $latex f(-x)=-f(x)$.
We observe that functions like $latex f(x) ={{x}^2}$ and $latex f(x)={{x}^4}$, where the exponent of x is even, will have the property that $latex f(x)=f(-x)$ since -1 raised to an even exponent equals 1.
Similarly, functions like $latex f(x)=x$ and $latex f(x)={{x}^3}$, where the exponent in x is odd, will have the property that $latex f(-x)=-f(x)$ given that -1 raised to an odd exponent is equal to -1.
Therefore, we have the following definitions:
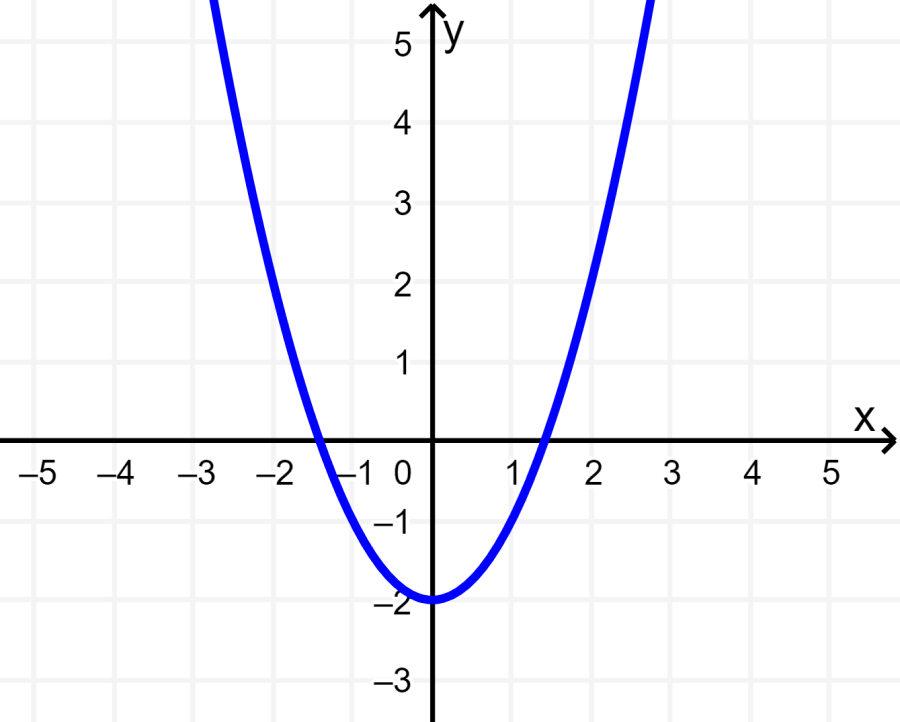
A function is even if $latex f(-x)=f(x)$. An even function has a reflection about the y-axis.
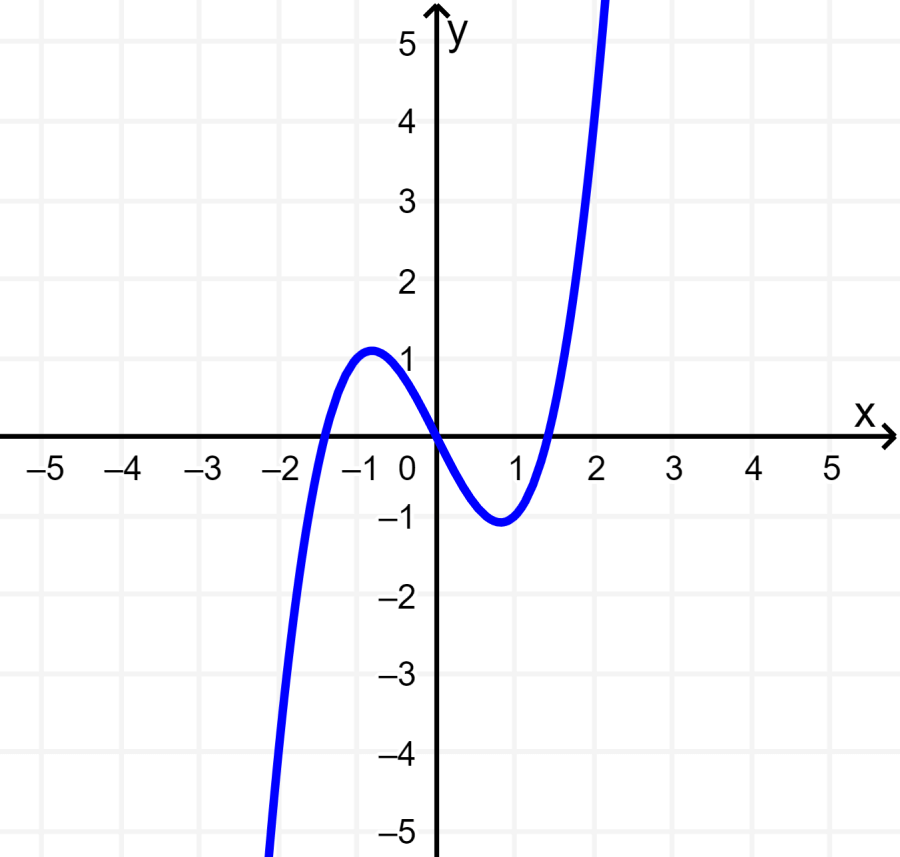
A function is odd if $latex f(-x)=-f(x)$. An odd function has rotational symmetry about the origin.
We can algebraically determine whether a function is even, odd, or none by replacing x with -x and calculating f (-x). If we have $latex f(-x)=f(x)$, the function is even. If we have $latex f(-x)=-f(x)$, the function is odd.
How to know if a function is symmetric about the origin?
Symmetry with respect to the origin is perhaps the most difficult to identify. To know if a function is symmetric with respect to the origin, we can identify several points on the graph since, in a function graph with symmetry with respect to the origin, we have the point (a, b) and the point (-a, -b).
For example, in the following graph, we have the points (2, 4) and (-2, -4). This means that the graph is symmetric with respect to the origin.
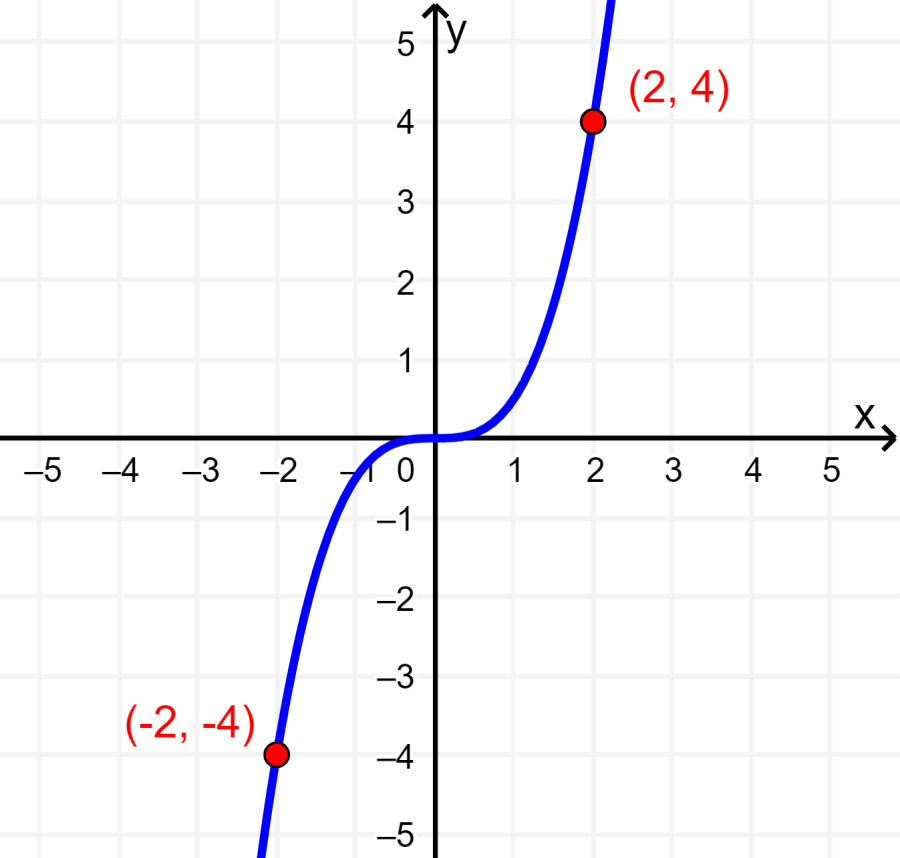
Test for symmetry about the origin
A graph will have symmetry with respect to the origin if we obtain an equivalent equation when all y‘s are replaced by -y and all x‘s are replaced by –x.
EXAMPLES
- Determine whether the function $latex y=2{{x}^3}-{{x}^5}$ is symmetric about the origin.
Solution: We have to replace x with -x and y with -y.
$latex y=2{{x}^3}-{{x}^5}$
$latex -y=2{{(-x)}^3}-{{(-x)}^5}$
$latex -5=-2{{x}^3}+{{x}^5}$
We can see that all the signs in this expression are exactly opposite to those in the original expression. This means that this expression is equivalent to the original expression since we can simply multiply the entire expression by -1 to get the original expression.
Examples of graphs with symmetry
In the description of the following graphs, it is shown whether there is any symmetry. Moreover, it is indicated if the graph represents a function.
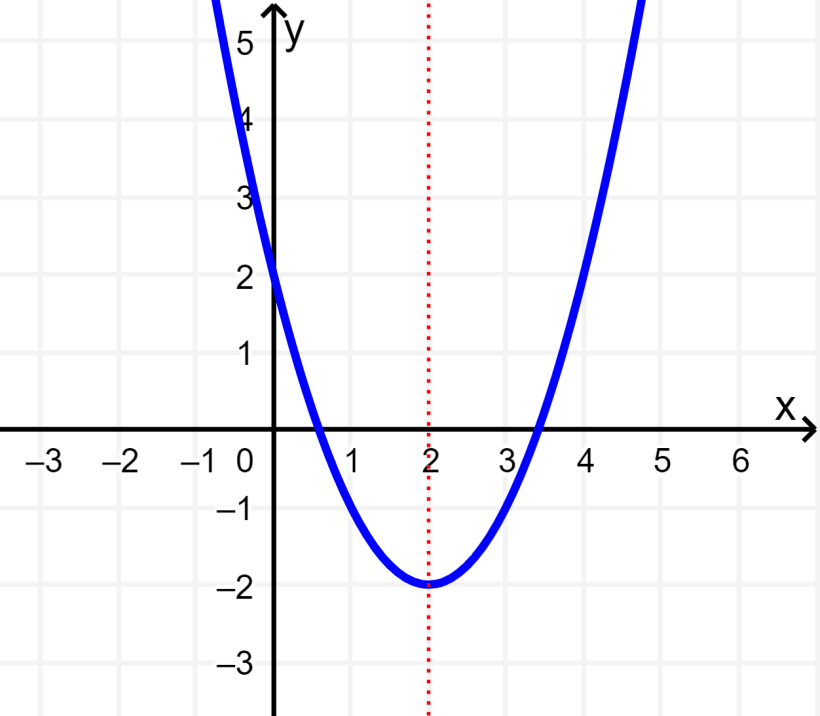
The following graph is symmetric about its axis, that is, it is symmetric about the line $latex x=2$. There is no other symmetry. The graph does represent a function.
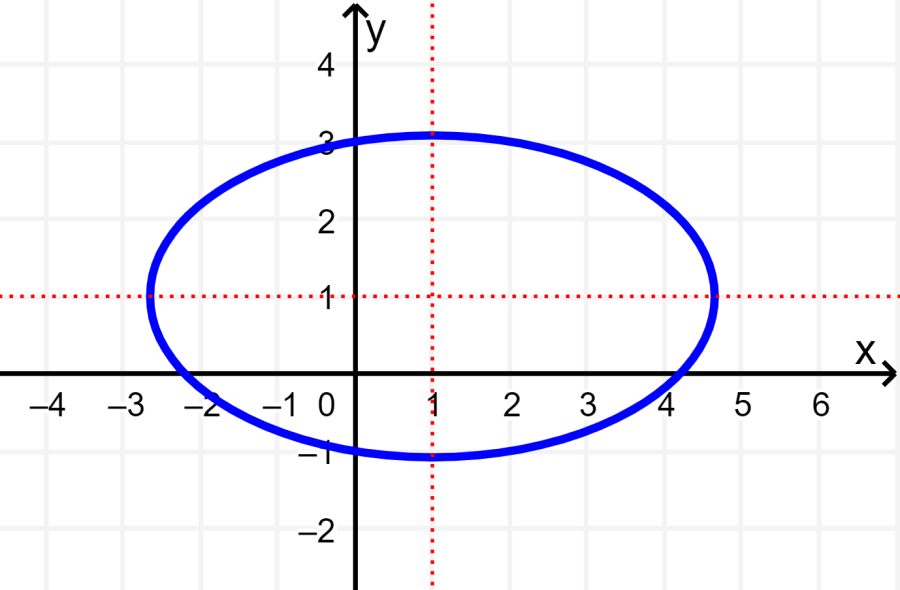
The graph below is symmetric about both the x-axis and the y-axis. This graph is also symmetric about the origin. Since the graph does not pass the vertical line test, that is, a vertical line can be drawn that passes through more than one point on the graph, then the graph does not represent a function.
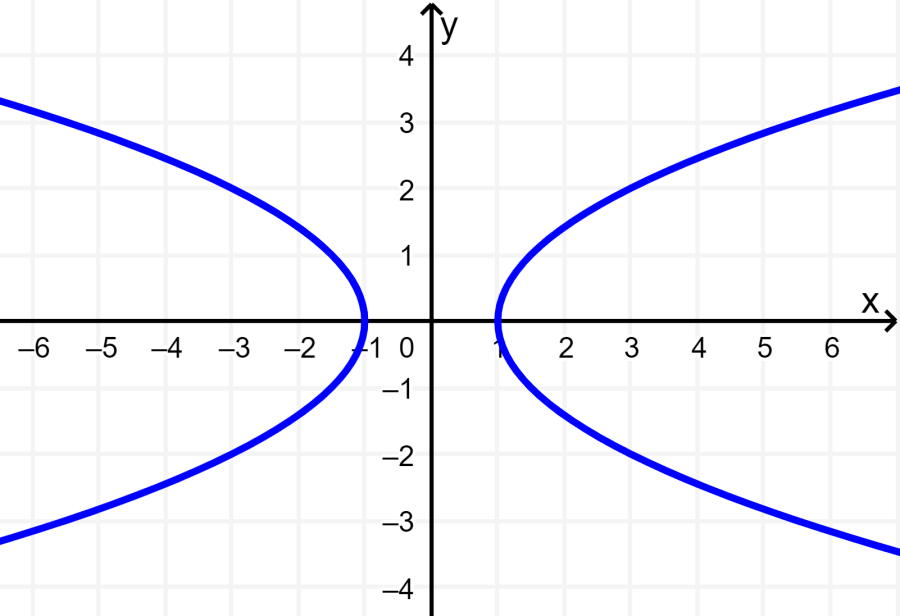
This graph is symmetric about the lines x=1 and y=1. Since a vertical line can be drawn that passes through more than one point on the graph, the graph does not represent a function.
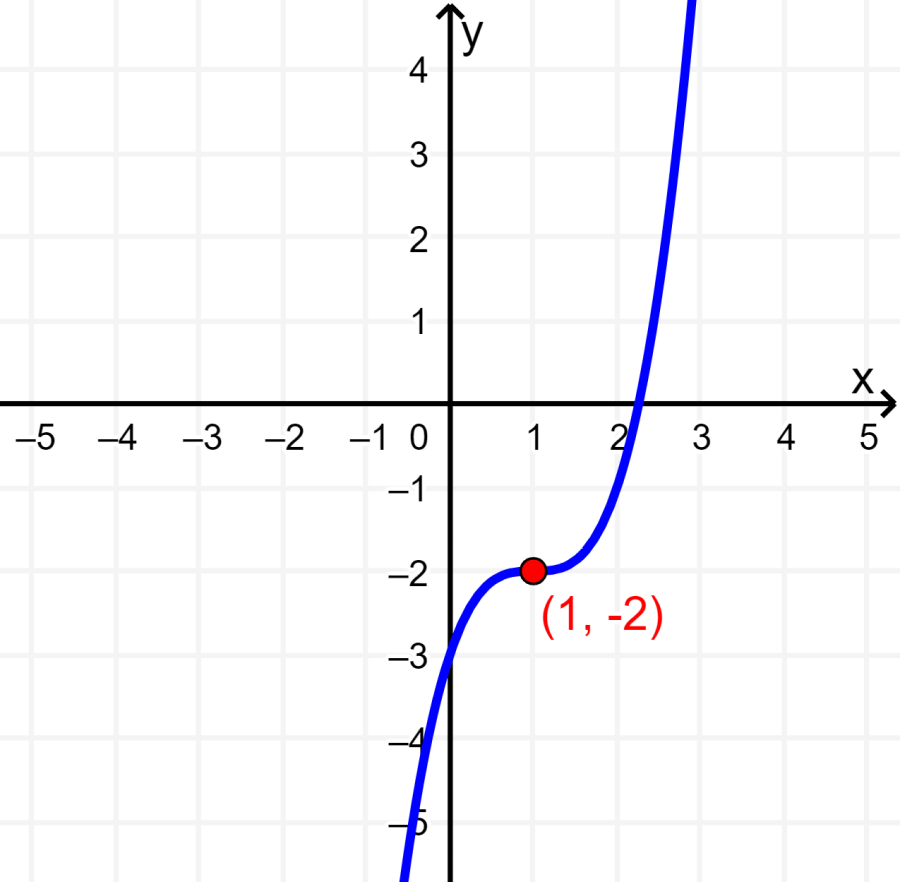
The graph below represents a cubic function that is symmetric about the point (1, -2). This graph does represent a function.
In the description of the following graphs, it is shown if the function is even, odd, or none.
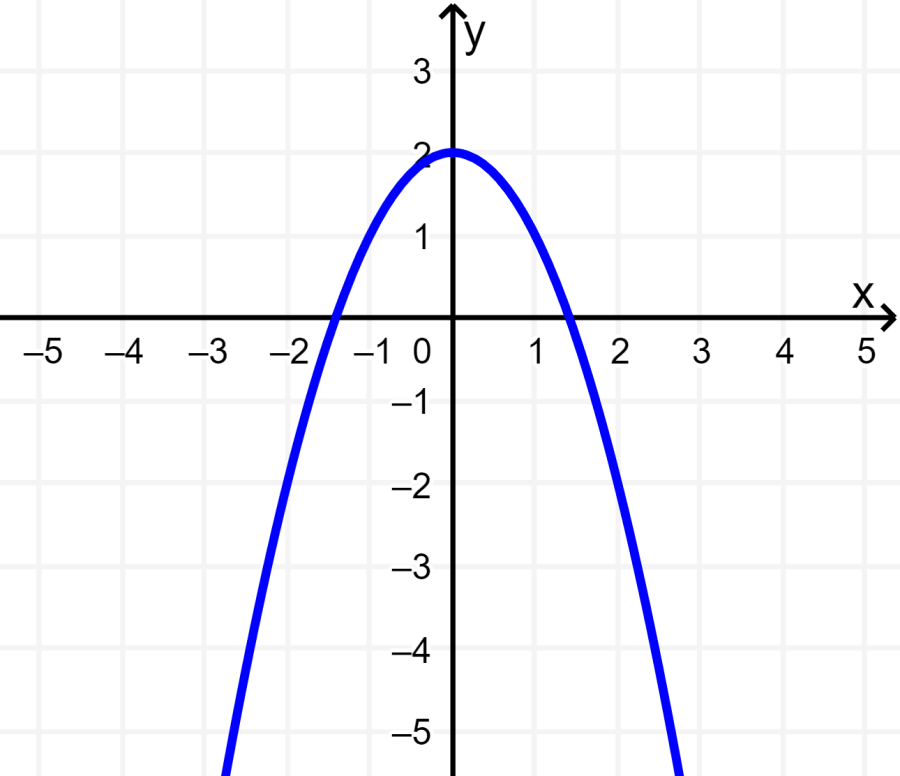
The following parabola has the vertex on the y-axis. This means that the axis of symmetry is the y-axis. Therefore, the function is even.
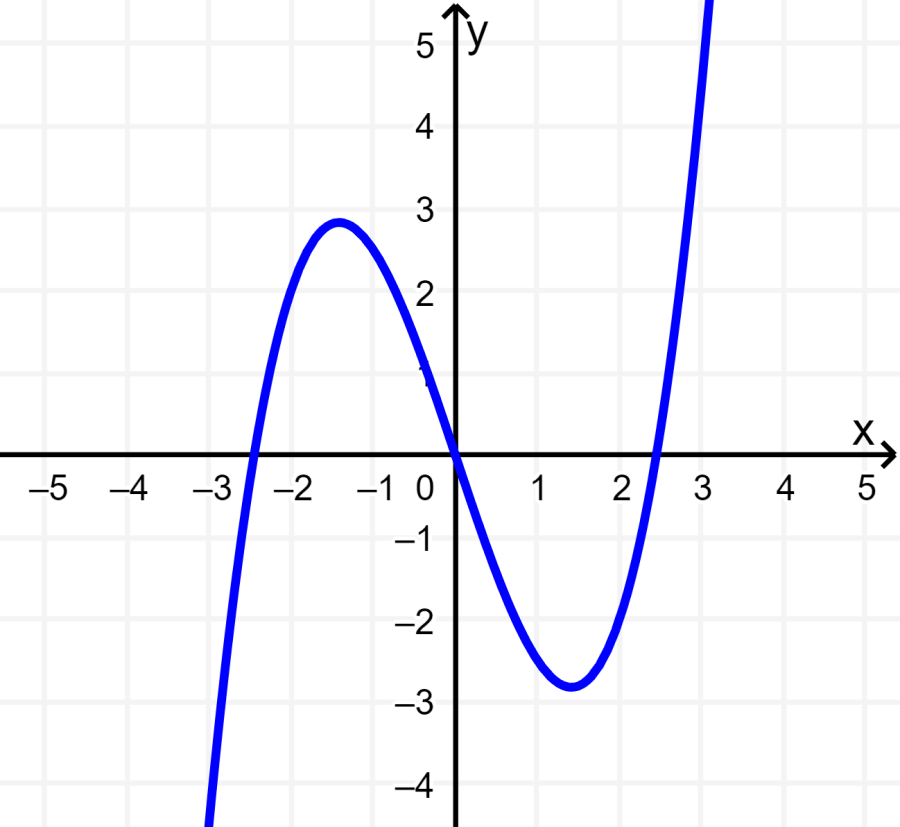
The following cubic function is centered at the origin and if we rotate it 180°, we will obtain the same graph. This means that the function is odd.
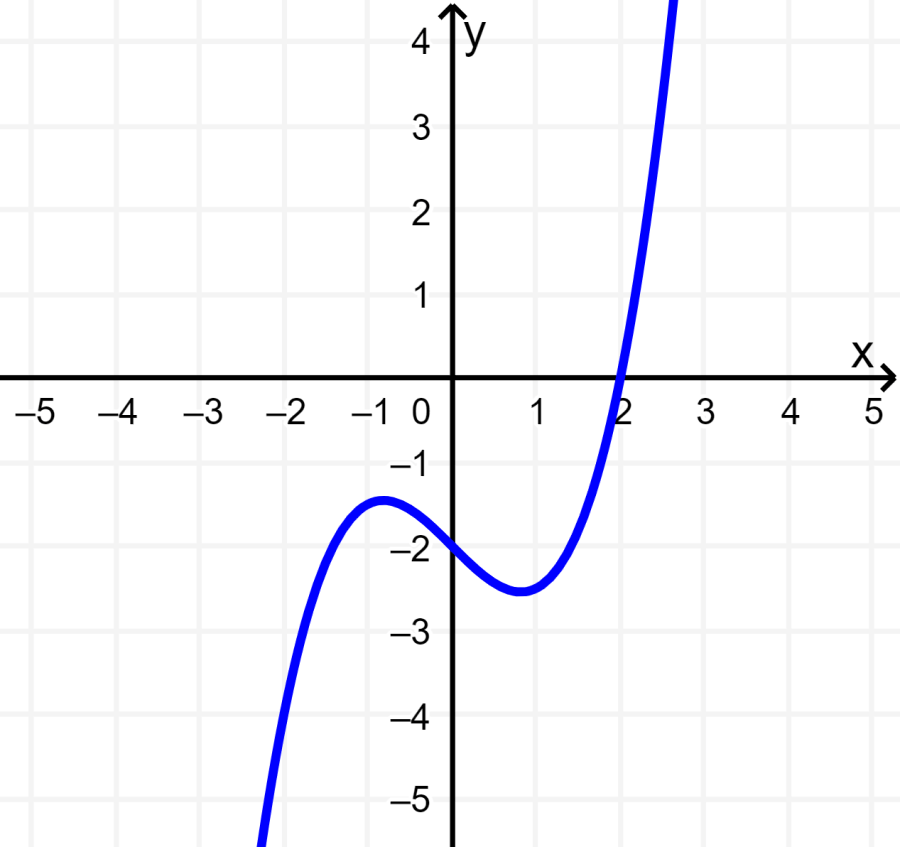
The following cubic function is centered at the point (0, -2). This function is symmetric, but not about the origin or the y-axis. Therefore, this function is neither even nor odd.
Symmetry of functions – Examples with answers
EXAMPLE 1
Determine if the function $latex f(x)=2{{x}^2}+5$ is symmetric.
Solution
Test 1:We start by checking if the function is symmetric with respect to the y axis. That means we have to replace all x with –x:
$latex f(-x)={{(-x)}^2}+5$
$latex ={{x}^2}+5$
After simplifying, we got the exact same function as $latex f(x)$, which means that they are both equivalents. Thus, this equation is symmetric with respect to the y-axis.
Test 2: Now, we check for symmetry with respect to the origin. This requires that we replace both x with –x and $latex f(x)$ with $latex -f(-x)$.
$latex -f(-x)={{(-x)}^2}+5$
$latex -f(-x)={{x}^2}+5$
In this case, the right side of the function is identical to the original but the left side is different since we have a minus sign in front.
EXAMPLE 2
Determine if the function $latex f(x)={{x}^3}+5x$ has some kind of symmetry.
Solution
Test 1: To determine if the function is symmetric with respect to the y-axis, we have to replace all x with –x:
$latex f(-x)={{(-x)}^3}+5(-x)$
$latex =-{{x}^3}-5x$
We see that we obtained an expression different from the original function on the right-hand side. This means that the function is not symmetric with respect to the y-axis.
Test 2: To check if the function is symmetric with respect to the origin, we have to change both to x with –x and $latex f(x)$ with $latex -f(-x)$.
$latex -f(-x)={{(-x)}^3}+5(-x)$
$latex -f(-x)=-{{x}^3}-5x$
$latex f(-x)={{x}^3}+5x$
We see that we got negative signs from both sides. By multiplying both sides by -1, we got the original function. This means that the function itself is symmetric with respect to the origin.
EXAMPLE 3
Has the function $latex f(x)={{x}^4}+2{{x}^3}+2x$ some kind of symmetry?
Solution
Test 1: We look for symmetry with respect to the y-axis by replacing all x with –x:
$$f(-x)={{(-x)}^4}+2{{(-x)}^3}+2(-x)$$
$latex ={{x}^4}-2{{x}^3}-2x$
After simplifying, we got a different expression than the original function, $latex f(x)$. Therefore, this equation has no symmetry with respect to the y-axis.
Test 2: We look for symmetry with respect to the origin by replacing both x with –x and $latex f(x)$ with $latex -f(-x)$.
$$-f(-x)={{(-x)}^4}+2{{(-x)}^3}+2(-x)$$
$latex -f(-x)={{x}^4}-2{{x}^3}-2x$
$latex f(-x)=-{{x}^4}+2{{x}^3}+2x$
If we multiply both sides of the function by -1, we do not obtain the original function, so this function does not have symmetry with respect to the origin.
EXAMPLE 4
Determine if the function $latex f(x)=3{{x}^4}-2{{x}^2}+4$ has some kind of symmetry.
Solution
Test 1: We start by looking for symmetry with respect to the y-axis. That means we have to replace all x with –x:
$latex f(-x)=3{{(-x)}^4}-2{{(-x)}^2}+4$
$latex =3{{x}^4}-2{{x}^2}+4$
We got exactly the same function as $latex f(x)$. Therefore, the function does have symmetry with respect to the y-axis.
Test 2: Now, we look for symmetry with respect to the origin. We need to replace both x with –x and $latex f(x)$ with $latex -f(-x)$.
$latex -f(-x)=3{{(-x)}^4}-2{{(-x)}^2}+4$
$latex -f(-x)=3{{x}^4}-2{{x}^2}+4$
$latex f(-x)=-3{{x}^4}+2{{x}^2}-4$
After multiplying by -1, we didn’t get the original function. This means that the function is not symmetric about the origin.
EXAMPLE 5
Is the function $latex f(x)={{x}^3}+{{x}^2}+x+1$ symmetric with respect to the y-axis or the origin?
Solution
Test 1: We check symmetry with respect to the y-axis by replacing all x with –x:
$$f(-x)={{(-x)}^3}+{{(-x)}^2}+(-x)+1$$
$latex =-{{x}^3}+{{x}^2}-x+5$
We see that we did not obtain the same function as the original function, $latex f(x)$, which means that the function is not symmetric with respect to the y-axis.
Test 2: We can check if the function has symmetry with respect to the original by replacing both x with –x and $latex f(x)$ with $latex -f(-x)$.
$$-f(-x)={{(-x)}^3}+{{(-x)}^2}+(-x)+1$$
$latex -f(-x)=-{{x}^3}+{{x}^2}-x+5$
$latex f(-x)={{x}^3}-{{x}^2}+x-5$
After simplifying and multiplying the function by -1, we did not obtain the original function, which means that it is not symmetric with respect to the origin. This function does not have any kind of symmetry.
This is not unusual since most functions do not have any kind of symmetry.
EXAMPLE 6
Determine if the function $latex f(x)=3{{x}^5}-4{{x}^3}+2x+4$ has some kind of symmetry.
Solution
Test 1: We replace all x with –x to look for symmetry with respect to the y-axis:
$$f(-x)=3{{(-x)}^5}-4{{(-x)}^3}+2(-x)+4$$
$latex =-3{{x}^5}+4{{x}^3}-2x+4$
After simplifying, we did not get the original function, which means that both are not equivalent and there is no symmetry with respect to the y-axis.
Test 2: We replace both x with –x and $latex f(x)$ with $latex -f(-x)$ to find symmetry with respect to the origin:
$$-f(-x)=3{{(-x)}^5}-4{{(-x)}^3}+2(-x)+4$$
$$-f(-x)=-3{{x}^5}+4{{x}^3}-2x+4$$
$$f(-x)=3{{x}^5}-4{{x}^3}+2x-4$$
We didn’t exactly get the original function, so the function is not symmetric about the origin.
Symmetry of functions – Practice problems
See also
Interested in learning more about functions? Take a look at these pages: