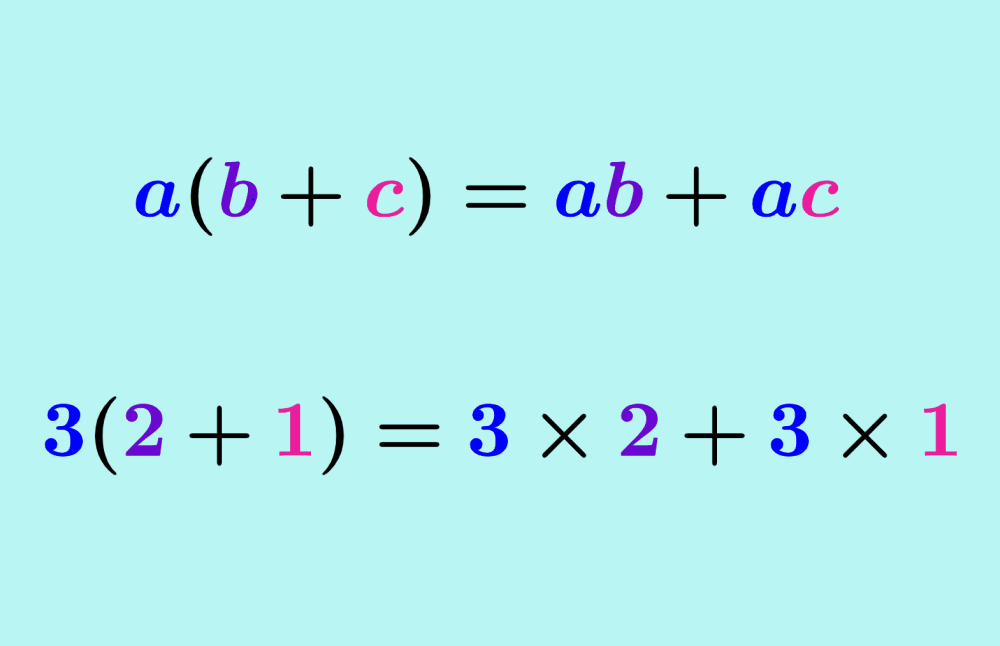The distributive property of multiplication is one of the most used properties in mathematics. This property tells us that when we have a multiplication of the form a(b+c), this is equivalent to ab+ac. The distributive property helps us simplify difficult problems by allowing us to rewrite expressions.
In addition, we will look at several examples with answers to fully master this topic. We will also see interactive problems to solve.
What is the distributive property of multiplication?
The distributive property is a mathematical property that indicates that the multiplication of a number by a sum of two or more terms is equal to the number multiplied by each addend.
That is, when we have a multiplication of the form a(b+c), the distributive property helps us solve it in the following way:
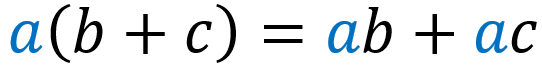
It doesn’t matter if we use the distributive property or follow the order of operations, we will always arrive at the same answer. In the following example, we simply follow the order of operations by simplifying what is inside the parentheses first.
$latex 5(4+3)=5(7)$
$latex =35$
Using the distributive property, we have the following:
$latex 5(4+3)=5( 4)+5(3)$
$latex =20+15$
$latex =35$
The distributive property for algebraic expressions
The distributive property is especially useful in algebra, as it allows us to simplify expressions with unknown values.
You might wonder why we don’t always follow the order of operations, which tells us to evaluate what’s inside the parentheses first. The answer is that there are times when we have variables and unlike terms inside the parentheses.
For example, if we have the expression $latex 5(x-2)+20$, we cannot add the x and -2 inside the parentheses because they are not like terms.
However, using the distributive property, we can simplify the expression as follows:
$latex 5(x-2)+20$
$latex =5(x)+5(-2)+20$
$latex =5x-10+20$
$latex =5x+10$
10 Examples of distributive property with answers
EXAMPLE 1
Solve the expression $latex 10(4+3)$ using the distributive property.
Solution
The distributive property tells us that we have to distribute the multiplication by 10 to each of the terms inside the parentheses. Thus, we have:
$latex 10(4+3)$
$latex =10(4)+10(3)$
$latex =40+30$
$latex =70$
EXAMPLE 2
Find the result of $latex 5(5-7)+3$.
Solution
We are going to use the distributive property to simplify the operation as follows:
$latex 5(5-7)+3$
$latex =5(5)+5(-7)+3$
$latex =25-35+3$
$latex =-10+3$
$latex =-7$
EXAMPLE 3
Find the result of $latex 5(3-4+5)$.
Solution
In this case, we have an addition of three numbers. Therefore, we distribute the multiplication by 5 to the three numbers in the parentheses:
$latex 5(3-4+5)$
$latex =5(3)+5(-4)+5(5)$
$latex =15-20+25$
$latex =-5+25$
$latex =20$
EXAMPLE 4
Use the distributive property to simplify the expression $latex 10(x+3)$.
Solution
We use the distributive property to distribute the 10 to the terms inside the parentheses:
$latex 10(x)+10(3)$
Now we multiply this and simplify:
$latex 10x+30$
EXAMPLE 5
Simplify the expression $latex 4x(2x+4)$.
Solution
We use the distributive property to distribute the 4x:
$latex 4x(2x)+4x(4)$
Now, we multiply and simplify:
$latex 8x^2+16x$
EXAMPLE 6
Use the distributive property to simplify the expression $latex 4(a+2)+2+a$
Solution
Applying the distributive property, we can write as follows:
$latex 4(a+2)+2+a$
$latex =4(a)+4(2)+2+a$
$latex =4a+8+2+a$
Now, we combine like terms:
$latex =(4a+a)+(8+2)$
$latex =5a+10$
EXAMPLE 7
Apply the distributive property on the expression $latex 5(5a-6)+4(2a+2)$.
Solution
We have multiplication by two parentheses. Therefore, we use the distributive property on both parentheses to get the following:
$latex 5(5a-6)+4(2a+2)$
$$=5(5a)+5(-6)+4(2a)+4(2)$$
$latex =25a-30+8a+8$
Now, we combine like terms to simplify:
$latex =(25a+8a)+(-30+8)$
$latex =33a-22$
EXAMPLE 8
Simplify the expression $latex -5y(3x-3y)$.
Solution
We distribute the -5y to the terms inside the parentheses without forgetting the sign change produced by the minus sign:
$latex -5y(3x)-5y(-3y)$
Now we just have to multiply and simplify:
$latex -15xy+15y^2$
EXAMPLE 9
Use the distributive property to simplify $latex 4x(3x+4y+5)$.
Solution
Here we distribute the multiplication by $latex 4x$ to the three terms inside the parentheses:
$latex 4x(3x)+4x(4y)+4x(5)$
Now we multiply and simplify:
$latex 12 x^2+16xy+20x$
EXAMPLE 10
Simplify the expression $latex 2x(5x^3+3x^2+5x)$.
Solution
We distribute the 2x to the three terms inside the parentheses:
$latex 2x(5x^3)+2x(3x^2)+2x(5x)$
We multiply and simplify:
$latex 10x^4+6x^3+10x^2$
→ Distributive Property Calculator
Distributive property – Practice problems


Use the distributive property to simplify the expression $$5(a+3)-4a+6(a-2)+2a-5$$
Write the expression in the input box.
See also
Interested in learning more about the distributive property and algebraic expressions? Take a look at these pages: