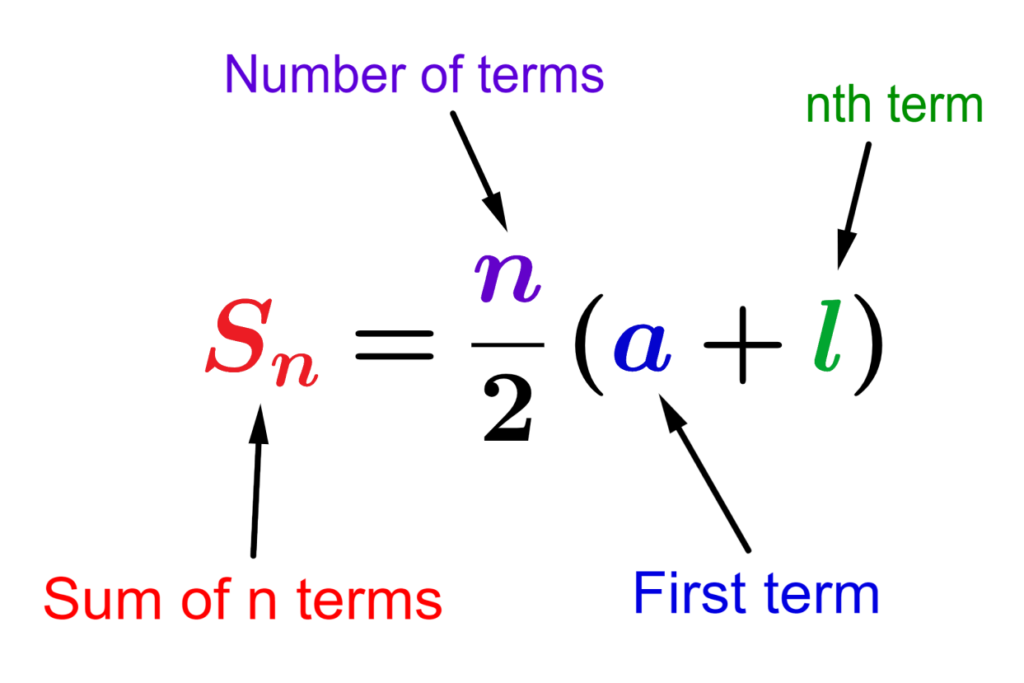The sum of an arithmetic sequence can be found using two different formulas, depending on the information available to us. Generally, the essential information is the value of the first term, the number of terms, and the last term or the common difference.
Here, we will solve several examples of the sum of arithmetic sequences. In addition, we will look some practice problems in which you can apply what you have learned.
Formulas for the sum of an arithmetic sequence
Arithmetic sequences are sequences in which their terms are formed from the previous term by adding a certain number called the common difference.
The sum of the first $latex n$ terms of an arithmetic sequence can be found with the following formula
$$S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}(a+l)$$
where,
- $latex a$ is the first term of the sequence.
- $latex l$ is the last term.
- $latex n $ is the number of terms.
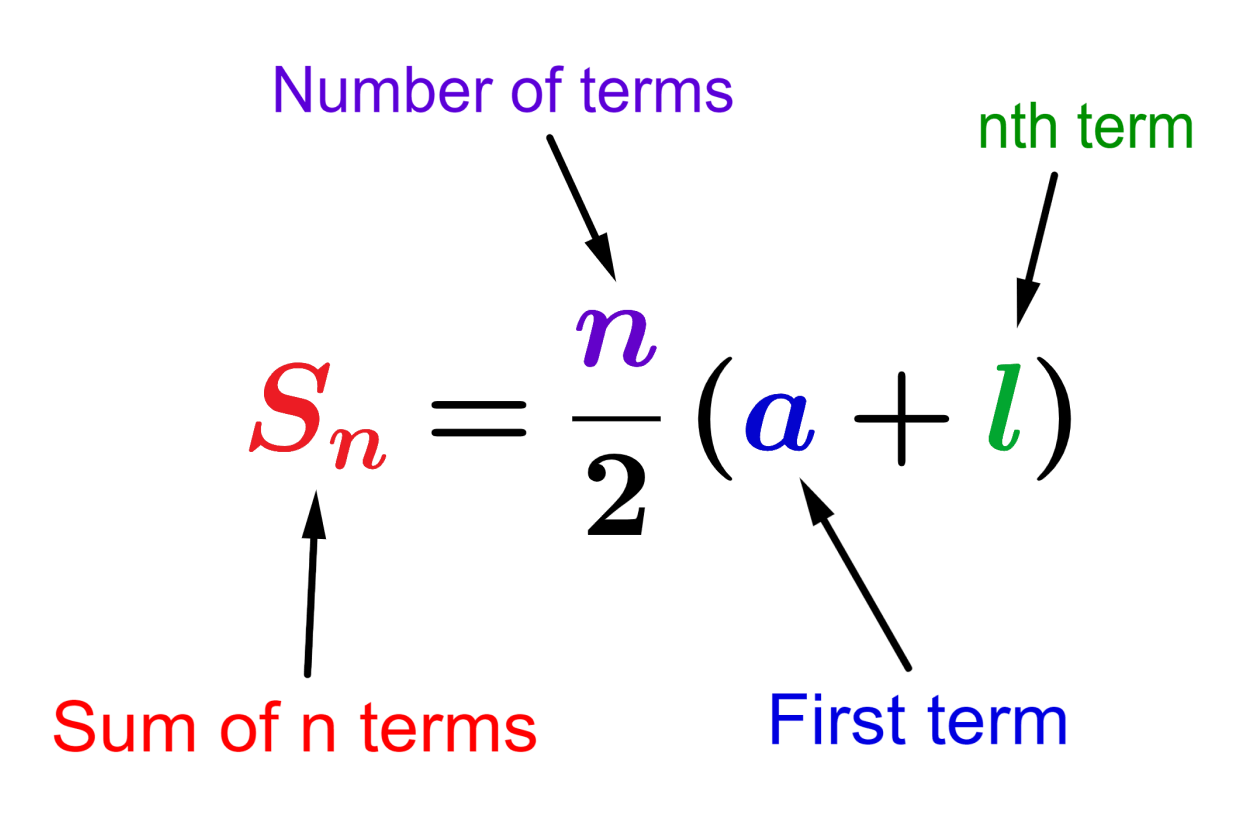
Also, remembering that any term of an arithmetic sequence can be found using the formula $latex a_{n}=a+(n-1)d$, we can write the formula for the sum as follows:
$$S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}[2a+(n-1)d]$$
where,
- $latex a$ is the first term.
- $latex d$ is the common difference.
- $latex n $ is the number of terms.
Proof of the formula for the sum of arithmetic sequences
Recall that each term of an arithmetic sequence is obtained by adding the common difference, d, to the previous term. Therefore, we can write the following:
$$S_{n}=a+[a+d]+…+[a+(n-1)d]$$
This is equation [1]. Now, we write the terms in reverse order, that is, from right to left.
$$S_{n}=[a+(n-1)d]+[a+(n-2)d]+…+a$$
This is equation [2]. If we add both equations, we can obtain the value of $latex 2S_{n}$:
$$2S_{n}=(a+[a+(n-1)d])+((a+d)+[a+(n-2)d])+…+([a+(n-1)d]+a)$$
$$2S_{n}=[2a+(n-1)d]+[2a+(n-1)d]+…+[2a+(n-1)d]$$
We can see that the terms obtained are equal, so the sum is equal to one of the terms multiplied by n (total number of terms).
$$2S_{n}=n[2a+(n-1)d]$$
Finally, we divide the entire equation by 2 to find $latex S_{n}$:
$$S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}[2a+(n-1)d]$$
10 Examples of sums of arithmetic sequences with answers
EXAMPLE 1
Find the sum of the first 8 terms of an arithmetic sequence, where the first term is 4 and the 8th term is 25.
Solution
We can start by writing all the values we know:
- First term: $latex a=4$
- Last term: $latex l=8$
- Number of terms: $latex n=8$
Now, we can use the formula for the sum of arithmetic sequences with the given values:
$$S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}[a+l]$$
$$S_{8}=\frac{8}{2}[4+25]$$
$$S_{8}=4[29]$$
$$S_{8}=116$$
EXAMPLE 2
The first term of an arithmetic sequence is 7 and the 15th term is 63. Find the sum of the first 15 terms.
Solution
We start by writing all the known values:
- First term: $latex a=7$
- Last term: $latex l=63$
- Number of terms: $latex n=15$
Now, we use the formula for the sum of an arithmetic sequence:
$$S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}[a+l]$$
$$S_{15}=\frac{15}{2}[7+63]$$
$$S_{15}=7.5[70]$$
$$S_{15}=525$$
EXAMPLE 3
Find the sum of the first 9 terms of an arithmetic sequence, where the first term is -20 and the 9th term is -44.
Solution
We have the following information:
- $latex a=-20$
- $latex l=-44$
- $latex n=9$
Using the formula for the sum with the given information, we have:
$$S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}[a+l]$$
$$S_{9}=\frac{9}{2}[-20-44]$$
$$S_{9}=4.5[-64]$$
$$S_{9}=-288$$
EXAMPLE 4
Find the sum of the first 20 terms of an arithmetic sequence starting with 5, 9, 13, 17, …
Solution
In this case, we don’t know the 20th term of the sequence. However, we can find the common difference by subtracting a term by its previous term.
Therefore, we have 9-5=4. And we have the following information:
- First term: $latex a=5$
- Common difference: $latex d=4$
- Number of terms: $latex n=20$
Now, we use this information in the second formula for the sum of an arithmetic sequence:
$$S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}[2a+(n-1)d]$$
$$S_{20}=\frac{20}{2}[2(5)+(20-1)4]$$
$$=10[10+(19)4]$$
$latex =10[10+76]$
$latex =10(86)$
$latex S_{20}=860$
EXAMPLE 5
An arithmetic sequence starts with the terms 60, 55, 50, … Find the sum of the first 12 terms.
Solution
We can find the common difference by subtracting a term by its previous term: 55-60=-5. Then, we have the following:
- $latex a=60$
- $latex d=-5$
- $latex n=12$
Now, we can use the second formula for the sum of an arithmetic sequence with the given information:
$$S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}[2a+(n-1)d]$$
$$S_{12}=\frac{12}{2}[2(60)+(12-1)(-5)]$$
$$=6[120+(11)(-5)]$$
$latex =6[120-55]$
$latex =6(65)$
$latex S_{12}=390$
EXAMPLE 6
Find the sum of the first 25 terms of an arithmetic sequence that starts with the terms 9, -1, -11, …
Solution
The common difference of the sequence is -1-9=-10. Then, we have the following values:
- $latex a=9$
- $latex d=-10$
- $latex n=25$
Now, we are going to use the second formula for the sum of an arithmetic sequence:
$$S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}[2a+(n-1)d]$$
$$S_{25}=\frac{25}{2}[2(9)+(25-1)(-10)]$$
$$=12.5[18+(24)(-10)]$$
$latex =12.5[18-240]$
$latex =12.5(-222)$
$latex S_{25}=2775$
EXAMPLE 7
What is the result of the following sum of the arithmetic sequence?
$$6+8+10+…30$$
Solution
We can start by finding the common difference of the sequence: 8-6=2. Then, we have:
- First term: $latex a=6$
- Common difference: $latex d=2$
- Last term: $latex l=30$
We don’t have the number of terms, so we can use the formula for the nth term to find it:
$latex a_{n}=a+(n-1)d$
$latex 30=6+(n-1)2$
$latex 24=(n-1)2$
$latex 12=n-1$
$latex n=13$
Now that we have all the required information, we can use the formula for the sum of arithmetic sequences:
$$S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}[a+l]$$
$$S_{13}=\frac{13}{2}[6+30]$$
$$S_{13}=\frac{13}{2}[36]$$
$$S_{13}=234$$
EXAMPLE 8
Find the sum of the following arithmetic sequence:
$$9+13+17+…+41$$
Solution
The common difference is equal to 13-9=4. Then, we have the following values:
- $latex a=9$
- $latex d=4$
- $latex l=41$
Now, we use the formula for the nth term to find the value of n:
$latex a_{n}=a+(n-1)d$
$latex 41=9+(n-1)4$
$latex 32=(n-1)4$
$latex 8=n-1$
$latex n=9$
Now that we have all the required information, we can find the sum of the sequence:
$$S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}[a+l]$$
$$S_{9}=\frac{9}{2}[9+41]$$
$$S_{9}=\frac{9}{2}[50]$$
$$S_{9}=225$$
EXAMPLE 9
What is the sum of the following arithmetic sequence?
$$62+60+58+…+38$$
Solution
The common difference of the sequence is equal to 60-62=-2. Then, we have the following values:
- $latex a=62$
- $latex d=-2$
- $latex l=38$
Now, let’s use the formula for the nth term to find the value of n:
$latex a_{n}=a+(n-1)d$
$latex 38=62+(n-1)(-2)$
$latex -24=(n-1)(-2)$
$latex 12=n-1$
$latex n=13$
Now, we find the sum with these values:
$$S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}[a+l]$$
$$S_{13}=\frac{13}{2}[62+38]$$
$$S_{13}=\frac{13}{2}[100]$$
$$S_{13}=650$$
EXAMPLE 10
If the first term of an arithmetic sequence is 2 and the nth term is 32, find the value of n if the sum of the first n terms is 357.
Solution
We can use the formula for the nth term with $latex a_{n}=32$:
$latex a+(n-1)d=32$
Also, since we know that the first term is 2, we have:
$latex 2+(n-1)d=32$
$latex (n-1)d=30~~[1]$
Now, we use the formula for the sum with the value $latex S_{n}=357$:
$$ \frac{n}{2}[2a+(n-1)d]=357$$
Since we know that $latex a=2$, we have:
$$ \frac{n}{2}[2(2)+(n-1)d]=357$$
$$ \frac{n}{2}[4+(n-1)d]=357~~[2]$$
Substituting equation [1] into equation [2], we have:
$latex n(4+30)=714$
$latex 34n=714$
$latex n=21$
Sum of arithmetic sequences – Practice problems


What is the result of the following sum of an arithmetic sequence? $$1.3+1.6+1.9+…+4.6$$
Write the answer in the input box.
See also
Interested in learning more about sequences? You can take a look at these pages: